Reading: Cell Structure Basics
Structures that are present in all cells – prokaryotic and eukaryotic
Cell Structure
-Cells resemble a plastic bag full of Jell-O with mixed fruit
-Can also think of a cell as your body – the skin holds everything in (cell wall), your bones provide structure (cytoskeleton), and your organs perform various functions (organelles)
-Parts of the cell common to all cells – prokaryotic and eukaryotic
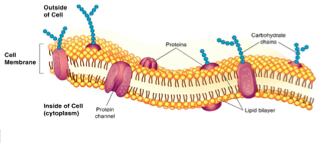
Plasma Membrane
Cytoplasm and cytoskeleton
DNA
Ribosomes
Plasma Membrane
-Forms barrier between the external environment which surrounds the cell and the inside of the cell (the bag around the Jell-O)
-Protects, supports, and controls what enters and exits the cell
-Formed by a phospholipid bilayer
Each phospholipid molecule has a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail which contributes to the
selectivity
-Also contains proteins and lipids essential for maintaining shape and transporting substances into and out of the cell
Cytoplasm and Cytosol
-Cytoplasm consists of everything inside the plasma membrane of the cell (the Jell-O and fruit inside the bag)
-Cytosol: the fluid in which organelles of the cell reside (the Jell-O)
-Functions:
Suspends organelles
Helps maintain cellular shape
Provides location for many biochemical reactions within the cell
Cytoskeleton
-Thread-like filaments and tubules that act as a cellular “skeleton” to help maintain cellular shape and hold organelles in place
-Organelles can move along the cytoskeleton
-Similar to your own skeleton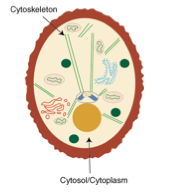
DNA
-A molecule that stores information, the cell’s “instruction manual”
-Contains all the information the cell needs to survive
Ribosomes
Organelles that produce proteins

