Reading: Chemistry of Life
Chemistry of Life
Why Chemistry?
All of life – cell functions, growing, reproducing is all dependent on the chemistry and chemical reactions that go on in the cell and between cellsThis will be a basic introduction into the main biologic macromolecules that make up life which will help your understanding of terms and ideas as we go forward
Four macromolecules
| Types of Compounds |
Examples | Functions |
|---|---|---|
| carbohydrates |
sugars, starches |
provides energy to cells, stores energy, forms body structures |
| lipids | fats, oils |
stores energy, forms cell membranes, carries messages |
| proteins | enzymes, antibodies |
helps cells keep their shape, makes up muscles, speeds up chemical reactions, carries messages and materials |
| nucleic acids |
DNA, RNA |
contains instructions for proteins, passes instructions from parents to offspring, helps make proteins |
Carbohydrates
-The most common type of organic (meaning making up living things) compound-Examples: sugars and starches
-Made of: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
-Functions: provides energy to cells, stores energy, and forms body structures
Lipids
-Examples: Fats and oils-Made of: carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
-Functions: stores energy, forms cell membranes, and carries messages
Proteins
-Examples: Enzymes, antibodies-Made of: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur
-Amino acids are joined together to make proteins
-Function: maintains cell shape, makes muscle tissue, speeds chemical reactions (enzymes), carries cellular messages
-The shape of a protein matches its function
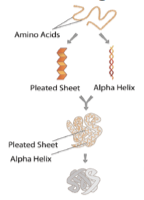
-There are 4 levels of organization/shapes of a protein:
Primary Protein Structure is sequence of a chain of amino acids.
Secondary Protein Structure occurs when the sequences of amino acids are linked by hydrogen
bonds.
Tertiary Protein Structure occurs when certain attractions are present between alpha helices and
pleated sheets.
Quaternary Protein Structure is protein consisting of more than one amino acid chain.
Nucleic Acids
-Example: DNA (double-stranded), RNA (single-stranded)-Made of: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus
Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of nucleic acids
-Function: stores genetic information and helps make proteins
Última modificación: lunes, 13 de agosto de 2018, 08:25
