Reading: Evolution Study Sheet
Big Picture
Key Terms
Evolution: Change in characteristics of living things over time.
Natural Selection: Organisms better fitted to the environment are more likely to survive and reproduce than organisms who aren’t fitted to the environment.
Fitness: How adapted an organism is to its environment.
Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics: Mistaken idea that animals whose traits changed in their lifetime could pass on those traits to their offspring. For example, a giraffe’s neck can extend its lifetime and pass the trait for long necks to its offspring.
Artificial Selection: A human practice to select certain traits wanted in a certain species.
Comparative Anatomy: Study of the differences and similarities between different species.
Homologous Structure: Organisms that have similar structures to organisms of other species because they descend from the same ancestor.
Analogous Structure: Animals with analogous structures inhabit the same types of environments, or perform tasks that require them to have a certain trait. These animals must then adapt, causing them to have similar traits that perform the same job, but this does not mean that their evolutionary history is related to each other.
Comparative Embryology: Study of the differences and similarities between different species as embryos.
Vestigial Structure: Structure found in an organism that has no obvious use.
Biogeography: The study of the environmental role of why animals live in a certain area.
Adaptive Radiation: Process by which a single species evolves into many
new species to fill available niches.
Darwin’s Theory
During Darwin’s trip to the Galápagos Islands located off the coast of South America, Darwin observed that the individual islands differed from each other in climate and soil. He also observed that the plants and animals on the islands differed. The tortoises on different islands had different shells, and it was possible to tell which island the tortoise came from by looking at the shell.Darwin’s observations helped him formulate his theory of evolution:
Artificial Selection
Humans can affect the evolution of a population or species by artificial selection. Artificial selection works much like natural selection does, but with humans, instead of nature, favoring specific traits.
For example, wolves were bred so that certain desirable traits would show up in the offspring. After thousands of years, these wolves evolved into the domesticated dogs we have today.
Evidence of Evolution
We can look at an animal’s evolutionary history by studying the fossil record.
• Example: The fossil record shows that the whale evolved from a land-dwelling creature.
We can also use comparative anatomy to compare one living species with another and figure out how these species evolved.
• Homologous structures, such as the forelimbs of mammals, suggest descent from a common ancestor. These structures may serve many different purposes, but they are still made up of similar parts.
• Analogous structures, such as the wings of bats and birds, have the same function, but examining the structures show that the organisms did not come from a common ancestor.
Comparative embryology compares living species at the embryo stage. Because embryos can have traits that do not appear in the organism in adulthood (vestigial structures), it is beneficial to compare embryos of different species because then one can tell if the two species ever had the same traits, or were related as a result of having the same traits.
• This is different from comparing species in adulthood because some vestigial structures disappear by adulthood.
• A vestigial structure means that the organism needed that particular trait before but the environment no longer calls for it.
• The human tail bone is an example of a vestigial structure.
DNA comparisons can also be used to understand how species evolved.
• DNA sequences can be used to estimate how long it has been since related species diverged from a common ancestor.
• Species with greater differences in their DNA sequences are assumed to have diverged from their common ancestor in the more distant past.
We can use biogeography to understand an animal’s environment and the environmental niche the animal must fill.
• By understanding the patterns of the environment, we can predict the types of evolutionary changes in a certain species, as the species must adapt to the environment as the environment changes.
• As many populations within one species migrate to different environments, these populations will all adapt to their respective environmental niches, and over time, these changes will bring about many new species.
• An example of adaptive radiation is the finches that Darwin discovered on his trip to the Galápagos Islands. He noticed that the birds on various Galápagos islands had differing traits, matched to the types of food the environment had. Darwin hypothesized that the birds had evolved to better fit the environment, and because the islands were separated and had slightly different food, the birds had different traits depending on the island.
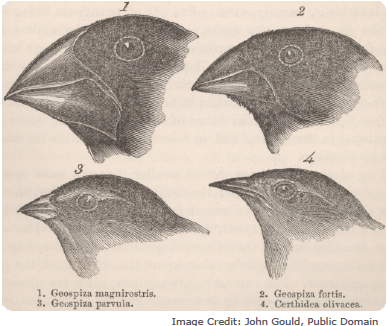
Figure: Here is a picture of the finches that Darwin observed on his trip to the Galápagos Islands. The beaks of the finches are slightly different from each other because each of the islands on the Galápagos have different environments and therefore different foods. The finches adapted to their respective environments, thus changing their physical features.
