Reading: Efficient Markets Hypothesis
Random
Walks and Efficient Markets
Random
Walk: the theory that stock price movements are unpredictable, so there is no way to know where prices are
headed.
- Studies of stock price movements indicate that they do not move in neat
patterns
- This random pattern is a natural outcome of markets that are highly efficient
and respond quickly to changes in material information
Random Walk

Efficient
Markets
•Efficient
Market: a market in which securities reflect all possible information quickly
and accurately.
•To
have an efficient market, you must have:
- Many knowledgeable investors actively analyzing and trading stocks
- Information is widely available to all investors
- Events, such as labor strikes or accidents, tend to happen randomly
- Investors react quickly and accurately to new information
- Many knowledgeable investors actively analyzing and trading stocks
- Information is widely available to all investors
- Events, such as labor strikes or accidents, tend to happen randomly
- Investors react quickly and accurately to new information
Efficient
Market Hypothesis
•Efficient
Market Hypothesis (EMH): information is reflected in prices – not only the type
and source of information, but also the quality and speed with which it is
reflected in prices. The more information that is incorporated into prices, the
more efficient the market becomes.
•Levels
of EMH
-Weak Form EMH
-Semi-strong Form EMH
-Strong Form EMH
-Weak Form EMH
-Semi-strong Form EMH
-Strong Form EMH
Weak
Form of EMH
•Weak
Form of EMH
- Past data on stock prices are of no use in predicting future stock price changes
- Everything is random
- Should simply use a “buy and hold” strategy
- Past data on stock prices are of no use in predicting future stock price changes
- Everything is random
- Should simply use a “buy and hold” strategy

Semi-strong
Form of EMH
•Semi-strong
Form EMH
- Abnormally large profits cannot be consistently earned using public information.
- Any price anomalies are quickly found out and the stock market adjusts
- Abnormally large profits cannot be consistently earned using public information.
- Any price anomalies are quickly found out and the stock market adjusts
Strong
Form of EMH
•Strong
Form EMH
- There is no information, public of private, that allows investors to consistently earn abnormally high returns.
- Seems to be evidence that the market is not strong form efficient
-Reason for inside trading laws
- There is no information, public of private, that allows investors to consistently earn abnormally high returns.
- Seems to be evidence that the market is not strong form efficient
-Reason for inside trading laws
Market
Anomalies
•Calendar
Effects
- Stock returns may be closely tied to the time of year or time of week.
- Questionable if really provides opportunity
- Examples: January Effect, weekend effect
- Stock returns may be closely tied to the time of year or time of week.
- Questionable if really provides opportunity
- Examples: January Effect, weekend effect
•Small-Firm
Effect
- Size of a firm impacts stock returns
- Small firms may offer higher returns than larger firms, even after adjusting for risk
- Size of a firm impacts stock returns
- Small firms may offer higher returns than larger firms, even after adjusting for risk
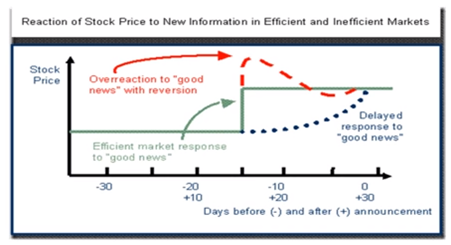
•Earnings
Announcements
- Stock price adjustments may continue after earnings adjustments have been announced
- Unusually good quarterly earnings reports may signal buying opportunity
- Stock price adjustments may continue after earnings adjustments have been announced
- Unusually good quarterly earnings reports may signal buying opportunity
•P/E
Effect (Value Effect)
- Uses P/E ratio to value stocks
- Low P/E stocks may outperform high P/E stocks, even after adjusting for risk
- Uses P/E ratio to value stocks
- Low P/E stocks may outperform high P/E stocks, even after adjusting for risk
Última modificación: martes, 14 de agosto de 2018, 08:46
