Reading: Stock Valuation
Facts
about Common Stocks
•Represents
ownership
•Ownership
implies control
•Stockholders
elect Board of Directors
•Directors
elect management
•Management’s
goal: Maximize stock price
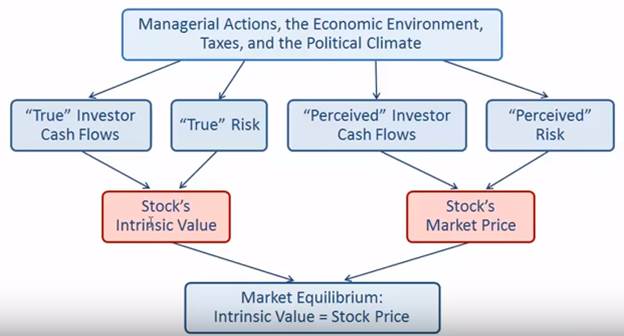
Intrinsic
Value and Stock Price
•Outside
investors, corporate insiders, and analysts use a variety of approaches to
estimate a stock’s intrinsic value (P0).
•In
equilibrium we assume that a stock’s price equals its intrinsic value.
- Outsiders estimate intrinsic value to help determine which stocks are attractive to buy or sell.
-Stocks with a price below (above) intrinsic value are undervalued (undervalued).
- Outsiders estimate intrinsic value to help determine which stocks are attractive to buy or sell.
-Stocks with a price below (above) intrinsic value are undervalued (undervalued).
Determinants
of Intrinsic Value and Stock Prices
Discounted
Dividend Model
•Value
of a stock is present value of the future dividends expected to be generated by
the stock.
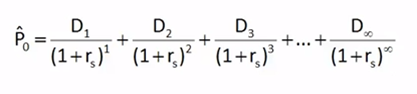
Constant
Growth Stock
A stock whose dividends are expected to grow forever at a constant rate, g.
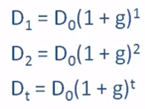
•If
g is constant, the discounted dividend formula converges to:
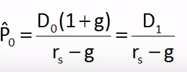
What
happens if g > rs?
•If
g > rs, the
constant growth formula leads to a negative stock price, which does not make
sense.
•The
constant growth model can only be used if:
- rs > g
- g is expected to be constant forever.
- rs > g
- g is expected to be constant forever.
Use
CAPM to Calculate the Required Rate of Return
•If
rRF =
7%, rM =
12%, and b = 1.2, what is the required rate of return on the firm’s stock?
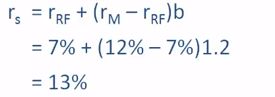
Find
the Expected Dividend Stream for the Next 3 Years and Their PV’s

Última modificación: martes, 14 de agosto de 2018, 08:49
