Reading: Maximizing Profit Under Competition
What
is Profit?
Profit = Total Revenue – Total
Costs
•Total
Revenue = Price
x
Quantity (P x
Q)
•Total
Costs has two parts
- Fixed costs are costs that do not vary due to output. (i.e. lease, most debt payments, etc.)
- Variable costs are costs that do vary with output. (i.e. electricity costs, transportation costs)
- Fixed costs are costs that do not vary due to output. (i.e. lease, most debt payments, etc.)
- Variable costs are costs that do vary with output. (i.e. electricity costs, transportation costs)
•Total
Costs = Fixed Costs + Variable Costs (Q)
The
Profit – Maximizing Quantity
•When
the firm produces an additional unit there are additional revenues and
additional costs
- Profit maximization is about comparing the additional revenue from selling an additional unit of output
- Marginal Revenue (MR) = the addition to total revenue from selling an additional unit of output
- Marginal Cost (MC) = the addition to total cost from producing an additional unit of output
- Profit maximization is about comparing the additional revenue from selling an additional unit of output
- Marginal Revenue (MR) = the addition to total revenue from selling an additional unit of output
- Marginal Cost (MC) = the addition to total cost from producing an additional unit of output
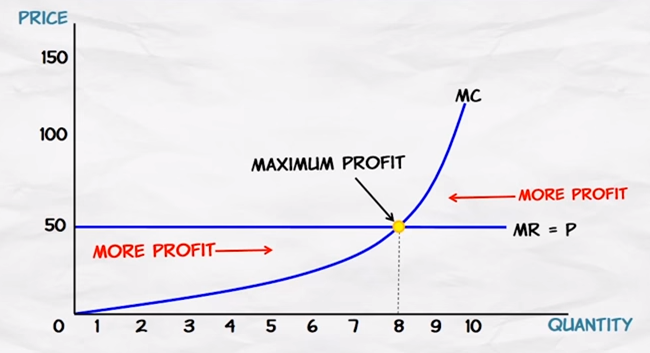
Maximizing
Profit
•Profits
are maximized at the level of output where MR = MC
- If MR > MC, you are not profit-maximizing, producing more will add to your profit.
- If MR < MC, you are not profit-maximizing, producing less will add to your profit
- Therefore, you can only profit-maximize if MR = MC
- If MR > MC, you are not profit-maximizing, producing more will add to your profit.
- If MR < MC, you are not profit-maximizing, producing less will add to your profit
- Therefore, you can only profit-maximize if MR = MC
The
Shape of MR and MC
•For
a firm in a competitive market, MR is constant and equal to Price because the
firm can sell any quantity at the market price
•MC
rises with production because it gets more costly to produce each additional
unit (i.e. more equipment, more maintenance, etc.)
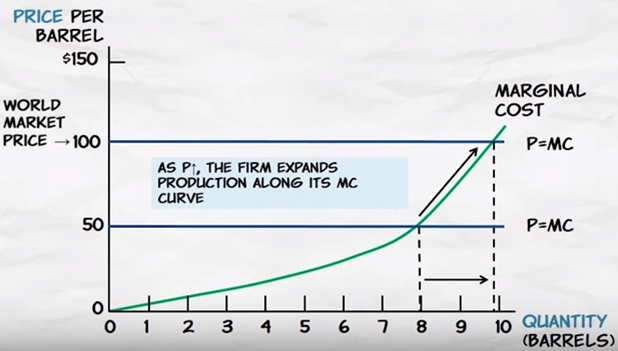
Maximizing
Profit Explains Behavior
Última modificación: martes, 14 de agosto de 2018, 10:18
