Reading: Perfect Competition in the Long Run
Adjustment
to Long Run Equilibrium
•If
most firms are making abnormal (economic) profits in the short run, this
encourages the entry of new firms into the industry driven into the market by
the profit motive
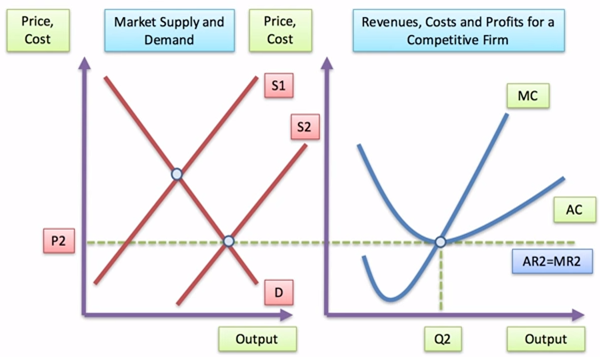
•This
will cause an outward shift in market supply forcing down the market price
•The
increase in market supply will eventually reduce the price until price = long
run average cost
•At
this point, each firm in the industry is making normal profit where price (AR)
= average cost
•Other
things remaining the same, there is no further incentive for movement of firms
in and out of the industry and long-run equilibrium has been established
The
Entry of New Firms in the Long Run
•At
this market price P1, most firms in the market make supernormal profits
•We
assume that the aim of each firm is to find a profit-maximizing output
•The
entry of firms causes an outward shift of market supply – price falls

Long
Run Equilibrium Price and Profit
•In
long run equilibrium all firms are making normal profits (P=AC)
•Normal
profits where AR=AC – i.e. just enough profits to keep resources in their
current use
Modifié le: mardi 14 août 2018, 10:21
