Slides: Thinking, Fast and Slow (Dr. Feddes)
By David Feddes
Think fast!
How
many animals of each kind did Moses take on the ark?
Think
fast!
A ball
and bat together cost $1.10.
The bat
costs $1 more than the ball.
How
much does the ball cost?
Think
fast!
In a
textile factory, 5 machines take exactly 5 minutes to make 5 shirts.
How
many minutes will it take for 100 machines to make 100 shirts?
Think fast!
A pond
has water lilies. Each day the flowers double the area they cover.
If it
takes 48 days for the pond to be completely covered, how many days would it
take to be half covered?
Think slow.
A pond
has water lilies. Each day the flowers double the area they cover.
If it
takes 48 days for the pond to be completely covered, how many days would it
take to be half covered?
Easy
answer: 24 Right answer: 47
Think slow
In a
textile factory, 5 machines take exactly 5 minutes to make 5 shirts. How many
minutes will it take for 100 machines to make 100 shirts?
Easy
answer: 100 Right answer: 5
Think slow
A ball
and bat together cost $1.10.
The bat
cost $1 more than the ball.
How
much does the ball cost?
Easy
answer: 10¢ Right answer: 5¢
Smart but wrong
80%+ of college students said 10¢.
50%+ of students at MIT, Harvard, and Princeton said 10¢.
Think slow
How
many animals of each kind did Moses take on the ark?
None.
Noah, not Moses, was on the ark.
Bible question
How
many animals of each kind did Noah take on the ark?
Easiest answer: Two
Most accurate answer: Seven
pairs of each kind of clean animal and one pair of each kind of unclean animal.
(Genesis 7:2)
Easy logic
All
roses are flowers.
Some
flowers fade quickly.
Therefore
some roses fade quickly.
Is this
argument logically valid?
- Easy but not valid. Perhaps no roses are among flowers that fade quickly.
- Slow down! Check the logic!
Key resource: Thinking, Fast and Slow, by Daniel Kahneman
System 1: Instant impressions

System 2: time and effort to figure out
17 x 23 =
17
x 23
51
34
391
Two systems
- System 1: fast, involuntary, automatic, effortless
- System 2: slow, deliberate, attentive, effortful
System 1 sample
- See one thing is closer than another
- Recognize face of person you know
- Sense anger in someone’s voice
- Answer 1 + 1= ?
- Drive car on road without traffic
- Understand simple sentences
System 2 sample
- Watch for someone at an airport
- Recall information for a test
- Control manners in a social setting
- Decide on a plan of action
- Evaluate complex logical argument
- Ponder how Bible applies now
Two systems
- System 1 has impressions, intuitions, intentions, feelings, desires
- System 2 usually believes System 1’s impressions and acts on System 1’s desires. System 2 takes over if System 1 is surprised or stumped.
Which horizontal line is longer?
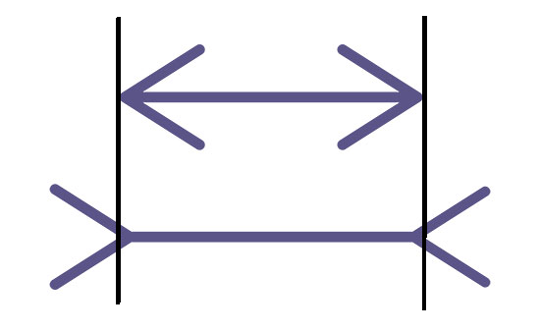

Bottom line still looks longer to System 1.
But System 2 now knows lines are equal.
Complementary roles
- System 1 (automatic reaction) and System 2 (attentive thinking) work well together much of the time.
- System 1 saves time and energy. Pondering every belief and decision would be too slow and exhausting.
- System 2 can evaluate as needed.
Beware of biases
- System 1 has built-in biases and tends toward systemic, frequently repeated errors in certain types of situation.
- System 2 is sometimes blind to biases of System 1 and accepts its errors rather than finding and fixing them.
Efficient jumping
Jumping to conclusions is efficient if the conclusions are likely to be correct and the costs of an occasional mistake acceptable, and if the jump saves much time and effort. (Daniel Kahneman)
System 1’s fast thinking is often right.
Risky jumping
Jumping to conclusions is risky when the situation is unfamiliar, the stakes are high, and there is no time to collect more information. (Daniel Kahneman)
In such situations, intuitive errors are more likely, and may be prevented by deliberate intervention of System 2.
Intuition or reason?
- If a belief or decision is minor, go with intuition. Don’t think too hard.
- If a belief or decision could have important, long-term impact, put time and effort into hard thinking.
- Train thinking skills so System 2 can work well when needed.
Smug slug
- System 2 feels in charge. But it’s lazy and prefers minimum effort.
- Some thoughts and actions that System 2 believes it rationally chose are prompted by System 1.
- Quick, easy answers feel right.
Smug slug
- Don’t be a slug. Think harder.
- Don’t be smug. Think humbler.
