Reading: Cornell Notes system
The Cornell Notes system (also Cornell note-taking system, Cornell method, or Cornell way) is a note-taking system devised in the 1940s by Walter Pauk, an education professor at Cornell University. Pauk advocated its use in his best-selling book How to Study in College.[1]
Overview of method
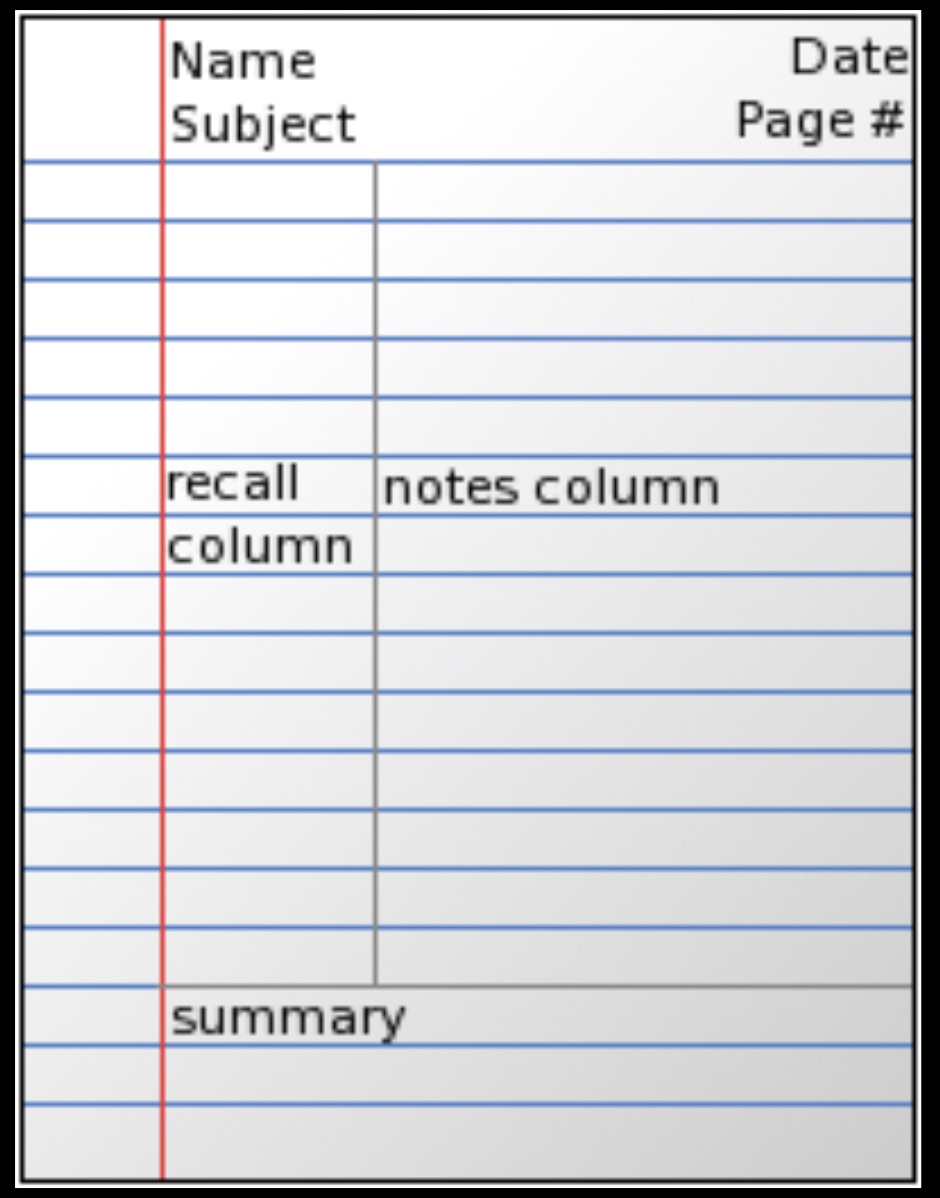
Notes Cornell
The Cornell method provides a systematic format for condensing and organizing notes. This system of taking notes is designed for a high school or college level student. There are several ways of taking notes, but one of the most common ones is the "two-column" notes. The student divides the paper into two columns: the note-taking column (usually on the right) is twice the size of the questions/keyword column (on the left). The student leaves five to seven lines, or about two inches (5 cm), at the bottom of the page.
Notes from a lecture or teaching are written in the note-taking column; notes usually consist of the main ideas of the text or lecture, and long ideas are paraphrased. Long sentences are avoided; symbols or abbreviations are used instead. To assist with future reviews, relevant questions (which should be recorded as soon as possible so that the lecture and questions will be fresh in the student's mind) or keywords are written in the keyword column. These notes can be taken from any source of information, such as fiction books, DVDs, lectures, textbooks, etc.[2]
When reviewing the material, the student can cover the note-taking (right) column while attempting to answer the questions/keywords in the keyword or cue (left) column. The student is encouraged to reflect on the material and review the notes regularly.[3]
Studies on effectiveness
A study published in 2010 by Wichita State University compared two note-taking methods in a secondary English classroom and found that Cornell Note-taking may be of added benefit in cases where students are required to synthesize and apply learned knowledge, while the guided notes method appeared to be better for basic recall.[4]
Another study published in the summer of 2013 found that "Students who were taught CN (Cornell notes) did take better notes than those who were not, but they did not have higher achievement results." The study also stated that "Through analysis of assessment scores, I found no significant difference between the intervention and base classes on achievement."[5]
Cornell note-taking can give students effectiveness in the organization of thoughts that they have been taught and give a better review in recollecting all the information that they have learned.[6] The Cornell note-taking system is not only a fast method of writing notes, but one is able to absorb the information that is given at a faster rate.[7]
This method can improve student's studying and listening skills.[8]
^ Pauk, Walter; Owens, Ross J. Q. (2010). How to Study in College (10 ed.). Boston, MA: Wadsworth. ISBN 978-1-4390-8446-5. Chapter 10: "The Cornell System: Take Effective Notes", pp. 235-277
^ "How to take notes as a law student - Becoming A Lawyer". Becoming A Lawyer. 2017-01-06. Archived from the original on 2017-09-05. Retrieved 2017-03-18.
^ Wong, Linda (2014-01-01). Essential Study Skills (8 ed.). Cengage Learning. p. 288. ISBN 978-1285430096.
^ Jacobs, Keil. A Comparison of Two Note Taking Methods in a Secondary English Classroom Proceedings: 4th Annual Symposium: Graduate Research and Scholarly Projects [79] Conference proceedings held at the Eugene Hughes Metropolitan Complex, Wichita State University, April 25, 2008. Symposium Chair: David M. Eichhorn
^ Broe, Duane (Summer 2013). "The Effects of Teaching Cornell Notes on Student Achievement" (PDF). www.minotstateu.edu/#. Retrieved 2017-05-12.
^ Quintus, Lori; Borr, Mari; Duffield, Stacy; Napoleon, Larry; Welch, Anita (Spring–Summer 2012). "The Impact of the Cornell Note-Taking Method on Students' Performance in a High School Family and Consumer Sciences Class" (PDF). www.natefacs.org. Retrieved 2018-10-10.
^ P, Mulder (2012). "Cornell Note Taking method (Cornell note taking method advantages)". Toolshero. Retrieved 2018-09-20.
^ Zulejka, Baharev (2016). The effects of Cornell note-taking and review strategies on recall and comprehension of lecture content for middle school students with and without disabilities (Thesis). Rutgers University - Graduate School of Education. doi:10.7282/T3HD7XZ8.
From Wikipedia
