Reading: Key Features of Bonds
What
is a Bond?
•A
long-term debt instrument in which a borrower agrees to make payments of
principal and interest, on specific dates, to the holder of the bonds.
Bond
Markets
•Primarily
traded in the over-the-counter (OTC) market.
•Most
bonds are owned and traded among large financial institutions.
•The
Wall Street Journal reports key developments in the Treasury, corporate, and
municipal markets.
Key
Features of a Bond
•Par
value: face amount of the bond, which is paid at maturity (assume $1,000).
•Coupon
interest rate: stated interest rate (generally fixed) paid by the issuer.
Multiply by par value to get dollar payment of interest.
•Maturity
date: years until the bond must be repaid.
•Issue
date: when the bond was issued.
•Yield
to maturity: rate of return earned on a bond held until maturity (also called
the “promised yield”).
Effect
of a Call Provision
•Allows
issuer to refund the bond issue if rates decline (helps the issuer, but hurts
the investor).
•Bond
investors require higher yields on callable bonds.
•In
many cases, callable bonds include a deferred call provision and a declining
call premium.
What
is a Sinking Fund?
•Provision
to pay off a loan over its life rather than all at maturity.
•Similar
to amortization on a term loan.
•Reduces
risk to investor, shortens average maturity.
•But
not good for investors if rates decline after issuance.
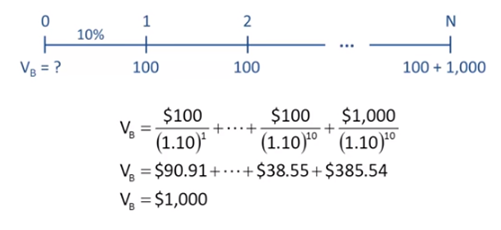
What
is the Value of a 10 year, 10% annual coupon bond, if rd =
10%?
Última modificación: martes, 14 de agosto de 2018, 08:42
