Reading: Tariffs and Protectionism
Analyzing
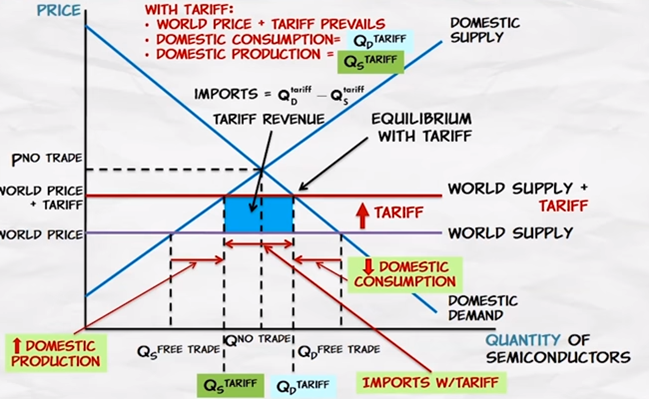
Tariffs with Supply and Demand
•Protectionism
– the economic policy of restraining trade through tariffs, quota’s or other
regulations that burden foreign producers but not domestic producers.
•Tariff
– a tax on imports.
•Quota
– restriction on the quantity of goods that can be imported.


The
(Net) Welfare Costs of Protectionism
•A
tariff has two effects that influence welfare:
1. Domestic consumption
2. Domestic production
Both
of these effects reduce welfare1. Domestic consumption
2. Domestic production
1. Domestic consumption
Lost gains from trade
2. Domestic production
Wasted resources from higher-cost production
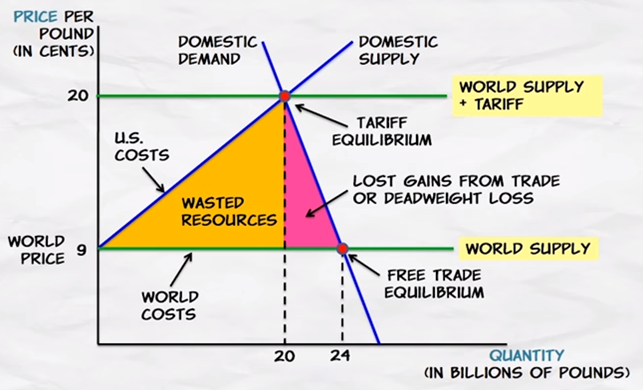

Conclusions
•Tariffs
increase prices to consumers so domestic consumption falls and creates a
deadweight loss.
•Tariffs
divert production from low-cost (world) producers to high-cost (domestic)
producers and this wastes resources.
•Distributions
of losses and gains
-Bad for consumers
-Good for domestic producers
-Bad overall
-Bad for consumers
-Good for domestic producers
-Bad overall
Última modificación: martes, 14 de agosto de 2018, 10:12
